|
Recommended Products
Vitamin C IV therapy has become increasingly popular over the last few years. A variety of micronutrient cocktails have been created with the goal to help support everything from dehydration and hangover to immune function and treating cancer.
About this item
500 Grams, MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane) Powder
Guaranteed 100% Pure. No Fillers or Additives.
Lab Tested and Verified.
Import Origin: USA.
Improves flexibility, Detoxifies the body, Strengthens hair and nails, Accelerates energy
|
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW LUNG CANCER - Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Lung carcinomas form from cells that line the airways of the lungs. The airways inside the lungs are the bronchi, bronchioli, and alveoli. NSCLC or Non Small Cell Lung Cancer is the most common type of lung cancer. Other lung carcinomas are neuroendocrine tumors.
Non Small cell Lung Cancer can be divided into early, locally advanced and metastatic.Early and locally advanced lung cancers means - cancer has not spread to the tissue lining around the lung or to other organs. The difference between early and locally advanced cancer is mainly based on the cancer stage. Early and locally advanced lung cancer is divided into cancer stages 1-3 out of which stage 1 is for early NSCLC and stage 2 and 3 are considered locally advanced and metastatic lung cancer is labelled as Stage 4. Metastatic NSCLC is lung cancer that has spread to other organs such as brain, liver, bone, and adrenal glands and from one lung to the other lung. Metastatic NSCLC also includes lung cancer that has spread to the lining of the lungs. The treatment team consists of : Pumlmonologist - an expert in lung diseases, Thoracic radiologist - an expert in imaging of the chest and Thoracic surgeon - an expert in operations within the chest Medical oncologist - an expert in systemic therapy (chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, etc) There’s no single treatment for NSCLC that’s best for everyone. Some people with early or locally advanced NSCLC have surgery to remove the cancer, whereas, other types of cancer treatment are used with surgery to improve results. Some early cancers are treated with radiation therapy,and others are treated with 2 types of treatments called chemoradiation - which includes both chemotherapy and radiation during the same period of time. Supportive care has been shown to extend and enhance life for people with lung cancer. It addresses the challenges of cancer.
Lung cancer screening is for people at high risk for lung cancer. When, some people with many risk factors never get lung cancer, some with no risk factors get lung cancer and experts are still learning why so. The biggest risk factor for lung cancer is smoking tobacco. There are more than 50 compounds in tobacco smoke known to cause cancer. The risk grows the more times a person smokes and the longer they smoke. Exposure to second-hand smoke increases the risk of lung cancer. Secondhand smoke is the smoke exhaled by another person and the smoke from the burning end of tobacco products.
MANAGEMENT OF NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
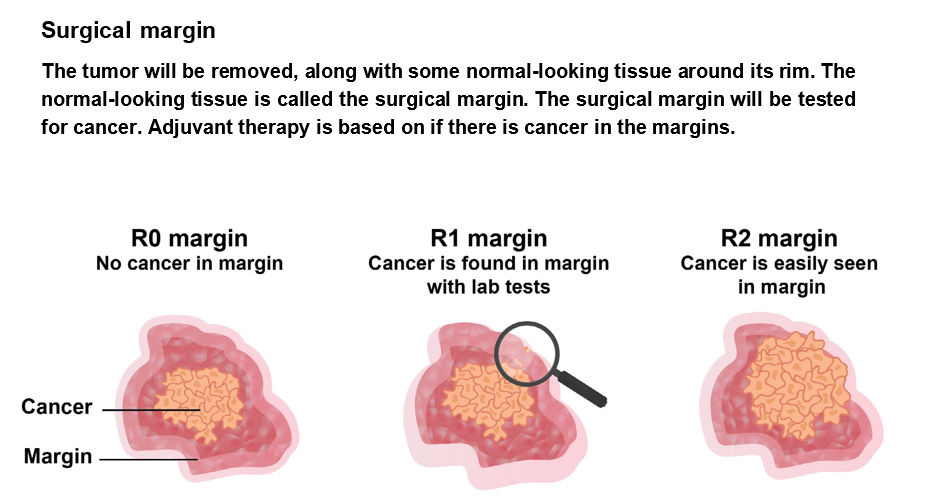
TNM (Tumour Nodes Metastasis ) system is used to score different areas of cancer growth. Lung cancer stages consist of combinations of TNM scores based on prognosis. A prognosis is the likely outcome of the cancer. For some people, lung cancer staging is done twice - 1) Clinical staging - cancer stage before treatment and 2) Pathological staging - occurs after surgery. It is based on tests of tissue removed from the body. Primary treatment is the main treatment used to rid your body of cancer. Not everyone with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) receives the same primary treatment. The treatment plan is based on many factors, including cancer stage, number of unrelated (primary) tumors, health of the patient. Types of primary treatment for early and locally advanced NSCLCSurgery is a treatment that removes tumors or organs with cancer. When possible, surgery is used as primary treatment to remove the tumour or organs with cancer. For many people, other types of treatments are received before or after surgery. The surgeon decides if one can safely undergo surgery based on whether the cancer is within the lung and outside the lung, the health of the lungs, overall health of the patient. There are five common lung cancer surgeries and the most common are lobectomy and pneumonectomy. A sleeve lobectomy removes a lobe and a part of the main airway called the bronchus. Wedge resection and segmentectomy remove only part of a lobe. Minimally invasive surgery for lung cancer is called thoracoscopy or video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS). Your surgeon may perform thoracoscopy using robotic arms to control the surgical tools.This approach is called robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS). Surgery is described as a complete resection when surgical margins, the furthest lymph nodes, and the fluid around the lungs and heart are cancer-free.Cancer that can be safely and completely removed is called resectable cancer. Resectable NSCLC is sometimes treated with more than one type of treatment. These other treatments are referred to as perioperative therapy. Treatment before surgery - Neoadjuvant therapy is a type of treatment that is received before surgery. It is sometimes called preoperative therapy or induction therapy. For NSCLC, neoadjuvant therapy consists of systemic therapy with or without radiation therapy. If you’ll likely need systemic therapy, you may receive it before surgery instead of after surgery. Neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy (Chemotherapy used with immunotherapy) is used to treat lung tumors that are at least 4 centimeters (cm) in size or lung cancer that has spread to lymph nodes. For some lung cancers, neoadjuvant therapy is given to shrink the cancer and make surgery easier. Perioperative therapy includes – chemotherapy, immunotherapy chemoimmunotherapy – combining both chemo and immunotherapy drugs, targeted therapy, radiation therapy and chemoradiation. Systemic therapy is commonly used for perioperative therapy. It is a whole-body treatment with cancer drugs. A medical oncologist is an expert in systemic therapy and can prescribe a regimen based on your overall health and the cancer. A regimen consists of one or more drugs that are taken at a specific dose, schedule, and length of time. Systemic therapy is drug treatment for metastatic lung cancer. Radiation therapy is sometimes used for perioperative therapy. Radiation therapy is called definitive radiation therapy, when the goal is to cure cancer. Chemoradiation is treatment with both chemotherapy and radiation therapy. When the goal is to cure cancer, chemoradiation is called definitive chemoradiation. Supportive care can relieve symptoms caused by cancer and its treatment. In case of invasive tumours(tumours that invade the tissue near the lungs), although not the preferred approach to surgery, concurrent chemoradiation or systemic therapy may be given. For certain other tumours based on the location (superior sulcus tumours), concurrent chemoradiation is the first treatment for superior sulcus tumors before surgery. Superior sulcus tumors are a distinct subset of invasive lung cancers. They start at the top of the lung and typically grow into the chest wall. Common side effects of any surgery are pain, swelling, and scars. Pain can be intense after lung surgery. Pain and swelling often fade away in the weeks after surgery.Numbness near the surgical area may be long-lasting. There is a chance of infection, which may cause pneumonia. There’s also a chance of a collapsed lung, which is called pneumothorax.After surgery, you may start adjuvant therapy or surveillance based on the staging of the cancer. Treatment after surgeryAdjuvant therapy follows the main treatment.It is also called postoperative therapy. It treats cancer that wasn’t removed during surgery and lowers the chance of cancer returning. Your care team will plan treatment based on several factors, including: ⮞ The status of the surgical margin—R0, R1, or R2 ⮞ The cancer stage after surgery, called the pathologic stage ⮞ Results of biomarker tests
RADIATION THERAPY EBRT (Externnal Beam Radiation Therapy) is used when trying to cure NSCLC. Any of the EBRT techniques described may be used, though SABR for early-stage cancer and IMRT for locally advanced cancer is typically preferrred. A lung tumor is harder to target than some other tumors in the body. Lung tumors often move when you breathe. To account for these challenges, advanced methods may be used: ⮞ Four-dimensional computed tomography (4D-CT) may be used for treatment planning. It’s like a video, so your radiation oncologist will see how the tumor moves when you breathe. ⮞ Motion control methods may be used to keep the tumor still during treatment. ⮞ At times, your radiation oncologist may ask you to hold your breath for 15 to 20 seconds at a time to better target the tumor. Radiation therapy does not cause pain during a treatment session—you'll feel nothing at all— and does not make you radioactive. Adding chemotherapy to radiation therapy often causes more side effects. -Fatigue is a common side effect of radiation therapy. -Skin changes in the treatment area may occur. Often, people describe skin changes as like a sunburn. For people with darker skin, radiation can cause the skin to darken and be painful. -Near the end of treatment, you may have pain when swallowing due to irritation to your esophagus. -Although not common, your lung may become inflamed after treatment causing sudden shortness of breath or cough. These are symptoms of radiation pneumonitis. and needs immediate medical help.
In case of metastatic lung cancer - Local treatment may be used for a specific area of metastatic cancer. It includes surgery, radiation therapy, and chemoradiation.
Local treatment is commonly used to reduce symptoms caused by metastasis. Less often, it is used to try to cure limited metastases. An example is cancer that has spread to only the brain or an adrenal gland. Consolidation treatmentThe goals of consolidation are to bolster the results of treatment and improve the chance of a cure. There are two options for consolidation treatment after definitive sequential chemoradiation: 1) Durvalumab (Immunotherapy) and 2)Osimertinib (EGFR Kinase Inhibitors) Common goals for healthy living include: ⮞ Seeing a primary care provider on a regular basis ⮞ Being physically active and avoiding inactivity ⮞ Eating healthful foods and limiting drinking alcohol ⮞ Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight ⮞ Not using tobacco ⮞ Avoiding infections and getting safe vaccines |
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW |
Oncology (Cancer) & Nuclear Medicine
This site has been developed for Cancer Patients & their Relatives under the 'Right of information for Patients'.
You may translate this page by clicking on the 'Select Language' - Top Left.