|
Recommended Products
Vitamin C IV therapy has become increasingly popular over the last few years. A variety of micronutrient cocktails have been created with the goal to help support everything from dehydration and hangover to immune function and treating cancer.
About this item
500 Grams, MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane) Powder
Guaranteed 100% Pure. No Fillers or Additives.
Lab Tested and Verified.
Import Origin: USA.
Improves flexibility, Detoxifies the body, Strengthens hair and nails, Accelerates energy
|
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW
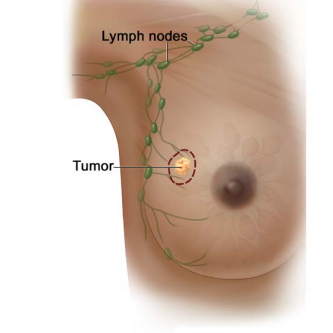
BREAST CANCER As per Global cancer statistics in 2022, breast cancer is the most common cancer in India, among women and the second most common cancer, when both the genders are considered. The breast is a glandular organ which is made up of milk ducts, fat, nerves, lymph and blood vessels, ligaments, and other connective tissue. Behind the breast is the pectoral (chest) muscle and ribs. Breast tissue contains glands that can make milk and they are called lobules. Small tubes called ducts connect the lobules to the nipple. Lymph fluid drains from breast tissue into lymph vessels and travels to lymph nodes near your armpit (axillary lymph nodes)
. Anyone can develop breast cancer, including males, but, treatment is very similar for both genders. DCIS or Ductal carcinoma insitu is a preinvasive disease, where the breast carcioma is found only in the cells that line the ducts and which has not spread to the surrounding tissue. Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare, aggressive cancer where cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This causes the breast to look red Mammogram - is a picture of the breast tissue using x-rays. During a mammogram, the breast is pressed between two plates while you stand in different positions. Multiple x-rays will be taken. A computer combines the x-rays to make detailed pictures. Screening mammograms are done on a regular basis when there are no signs or symptoms of breast cancer. Diagnostic mammograms are used for Results from biopsy and imaging studies will be used to determine your treatment plan. Treatment will be based on these findings.
Clinical breast exam (CBE) is a physical exam of the bare breast performed by a health care provider to check for lumps or other changes. It is done while you are seated and/or lying down. Your provider should take time to palpate (feel) the entire breast, including the armpit. A nurse or assistant might also be in the room during the exam. The testing and confirmation of the diagnosis of breast cancer takes time - might take days or weeks for all the test results to come. There are various possible biopsies which may include FNA or Core BIopsy, Incisional biopsy or Excisional biopsy.
About 1 out of 10 breast cancers are hereditary. Depending on the family history or other features of cancer, onemight require hereditary genetic testing to learn more about your cancer. Genetic testing is done collecting blood or saliva (spitting into a cup or a cheek swab). The goal is to look for gene mutations inherited from your biological parents called germline mutations. Some mutations can put you at risk for more than one type of cancer and can also, pass these genes to their children. Also, other blood relatives might carry these mutations, therefore, the family history of cancer iis of utmost importance. Everyone has BRCA genes. Normal BRCA genes help to prevent tumor growth. They help fix damaged cells and help cells grow normally. BRCA mutations put you at risk for more than one type of cancer. Mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 increase the risk of breast, ovarian, prostate, colorectal, pancreatic, and melanoma skin cancers. Breast cancer staging is often done twice --> Clinical stage (c) is the rating given before any treatment. It is based on a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. The staging system helps to determine how much cancer is in your body, where it is located, and what subtype of cancer the patient has.The grade of tumour describes how abnormal the tumor cells look under a microscope. Higher-grade cancers tend to grow and spread faster than lower-grade cancers. The stages of breast cancer can be divided as Stage 0,1,2,3, and 4. Stage 0 is noninvasive – DCIS is found only in the cells that line the ducts. In DCIS, the cancerous cells are in place (in situ) and has not spread to the surrounding breast tissue or lymph nodes or distant sites and have not spread outside the ducts. DCIS is a preinvasive disease and is treated to prevent invasive cancer (a more advanced form of cancer). Stages 1, 2, and 3 are invasive – It has grown outside the ducts, lobules, or breast skin, into the surrounding breast tissue or nearby lymph nodes. Cancer that has spread to a nearby body part such as the axillary lymph nodes is called a local metastasis. It might be referred to as local/regional disease or locally advanced. Invasive breast cancer is treatable. Treatment usually involves - local(surgery, radiation therapy), systemic, or usually a combination of both. Stage 4 is when cancer has spread to distant sites (a body part far from the primary tumor). It can develop from earlier stages or rarely, the first diagnosis can be stage 4 metastatic breast cancer. Breast cancer can metastasize almost anywhere but most commonly spreads to the bone (including spine), lungs, liver, brain, or distant lymph nodes. During staging, the following things are considered : ⮞ The extent (size) of the tumor ⮞ The spread to nearby lymph nodes ⮞ The spread (metastasis) to distant sites ⮞ Estrogen receptor (ER) status ⮞ Progesterone receptor (PR) status ⮞ Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status ⮞ Grade of the cancer ⮞ Biomarker testing
In breast cancer, there are Clinical and Pathological staging. Clinical staging is done before any treatment. It is based on a physical exam, biopsy, and imaging tests. Pathologic staging or surgical staging is determined by examining tissue removed during surgery.
TREATMENT: The treament decisions are taken by a team of doctors which constitute the Multidisciplinary team (MDT), based on the stage of the tumour and patient fitness and many other factors. Local therapy: - focuses on the breast, chest wall, and lymph node area. It includes: ⮞ Surgery (lumpectomy, mastectomy, and lymph node surgery) ⮞ Radiation therapy Systemic therapy: works throughout the body. It includes: ⮞ Chemotherapy ⮞ HER2-targeted therapy ⮞ Inhibitors or other targeted therapies ⮞ Immunotherapy ⮞ Endocrine therapy Surgery is the main or primary treatment for DCIS, among the various treatment options available. SURGERY : Surgery is an operation or procedure to remove cancer from the body. The goal of surgery or tumor resection is to remove all the cancer. The tumor is removed along with a rim of normal-looking tissue around its edge called the surgical margin. The surgical margin may look normal during surgery, but cancerous cells may be found when viewed under a microscope on examination by a pathologist. It is said to have a clear or negative margin, if no cancer cells are found in the tissue around the edge of the tumor. In a positive margin, cancer cells are found in normal looking tissue around the tumor. After surgery, one might have to receive treatment such as radiation to kill any remaining cancer cells. Also, there might be a wound drain to prevent fluid from collecting in the body after surgery. These drains are usually removed a few days after surgery.
The dotted line in the above picture shows where the tumor is removed. Lumpectomy is the removal of abnormal cells or tumor and not the whole breast. It is also known as Breast conservation surgery.
There are different types of mastectomies which include total mastectomy or simple mastectoy, skin-spring mastectomy and nipple sparing mastectomy. Breast reconstruction is an option after a mastectomy. It might be done at the same time as mastectomy (immediate) or at some time following the completion of cancer treatment (delayed). Before removing the breast, the surgeon may do a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). Sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) are the first lymph nodes cancer cells are likely to have spread to from the primary tumor. It helps to determine if any cancer cells have traveled to the lymph nodes. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) is surgery to remove axillary lymph nodes. This is performed after an axillary lymph node biopsy or SLNB shows cancer in the lymph nodes (called node positive). Then, an ALND will remove any other lymph nodes that contain cancer. Removing axillary lymph nodes can cause lymphedema of the upper limb. Surgery is the main or primary treatment for invasive breast cancer, which constitute only one part of the treatment plan. SYSTEMIC THERAPY : Systemic (drug) therapy might be used before surgery to shrink the tumor or reduce the amount of cancer (called cancer burden). ⮞ Preoperative or neoadjuvant therapy is systemic treatment before surgery. ⮞ Postoperative or adjuvant therapy is systemic treatment after surgery. Systemic therapy includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy and endocrine therapy. CHEMOTHERAPY:Chemotherapy is often the first treatment for hormone receptor-negative (HR-) cancers. ENDOCRINE THERAPY : There are 4 hormones that might be targeted in endocrine therapy for breast cancer. It includes : Estrogen, Progesterone, Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) and Androgen. Hormones may cause breast cancer to grow. Endocrine therapy will stop your body from making hormones or it will block what hormones do in the body. This can help to reduce the risk of cancer returning. Endocrine therapy is sometimes called hormone therapy. HR+ breast cancer is treated with endocrine therapy, which blocks estrogen receptor signaling or decreases estrogen production. Ovarian suppression or ablation is also considered for higher risk Estrogen receptor positive breast cancer patients. Some treatments for breast cancer, like aromatase inhibitors or GnRH agonists, can cause bone loss, which puts you at an increased risk for fractures. Drugs used to prevent bone loss and fractures include: ⮞ Oral bisphosphonates ⮞ Zoledronic acid ⮞ Pamidronate ⮞ Denosumab The patient will be screened for bone weakness (osteoporosis) using a bone mineral density test. This measures how much calcium and other minerals are in your bones. It is also called a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan and is painless. Bone mineral density tests look for osteoporosis and help predict your risk for bone fractures. A baseline DEXA scan is recommended before starting endocrine therapy. BIOMARKER TESTING :Biomarker testing includes tests of genes or their products (proteins). It identifies the presence or absence of mutations and certain proteins that might suggest treatment RADIATION THERAPY (RT) - uses high-energy radiation from x-rays (photons), protons, and other sources to kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery. Different types of radiation can be used for treatment of breast cancer based on the final diagnosis and the type of surgery doe. Types of radiation therapy used include: -Whole breast radiation therapy (WBRT) is used to treat the entire breast.Sometimes, additional treatments may be given to the tumor area. This is called a
SUPPORTIVE CARE: It is health care given to prevent, reduce, and relieve suffering, and to improve quality of life. Supportive care might include pain relief, palliative care, emotional or spiritual support, financial aid, or family counseling. Therefore, proper communication needs to be there with the patient and the treating team, so that timely intervention is done. Side effects : All cancer treatments can cause unwanted health issues called side effects. Side effects depend on many factors, which include the drug type and dose, length of treatment, and the patient. Some side effects may be harmful to the patient, others may just be unpleasant. There can be acute side effects, which may occur at the time of treatment or during the treatment time. Late side effects may occur months or years after a disease is diagnosed or after treatment has ended. Late effects may be caused by cancer or cancer treatment. Some of them may be temporary and some may be permanent. Some of the side effects may include : Lymphoedema, nausea and vomiting, neurocognitive or neuropsychological effects, neuropathy,pain, blood clots, bone weakness/ osteoporosis, hairloss, low blood cell counts difficulty in eating and loss of appetite, fatigue, mental distress, diarrhoea,etc. RECURRENCE: It is when cancer returns after complete treatment .Treatment is based on the types of treatment you had before. Together, you and your care team will choose a treatment plan that is best for you. SURVIVORSHIP : A person is a cancer survivor from the time of diagnosis until the end of life. After treatment, the health will be monitored for side effects of treatment and the return of cancer. This is part of your survivorship care plan. It is important to keep any follow-up doctor visits and imaging test appointments. Seek good routine medical care, including regular doctor visits for preventive care and cancer screening.
|
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW |
Oncology (Cancer) & Nuclear Medicine
This site has been developed for Cancer Patients & their Relatives under the 'Right of information for Patients'.
You may translate this page by clicking on the 'Select Language' - Top Left.