|
Recommended Products
About this item
500 Grams, MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane) Powder
Guaranteed 100% Pure. No Fillers or Additives.
Lab Tested and Verified.
Import Origin: USA.
Improves flexibility, Detoxifies the body, Strengthens hair and nails, Accelerates energy
Vitamin C IV therapy has become increasingly popular over the last few years. A variety of micronutrient cocktails have been created with the goal to help support everything from dehydration and hangover to immune function and treating cancer.
|
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW
1. Types of Cancer >
3. Solid Tumors
These are tumors that form solid masses and are usually associated with specific organs or tissues.
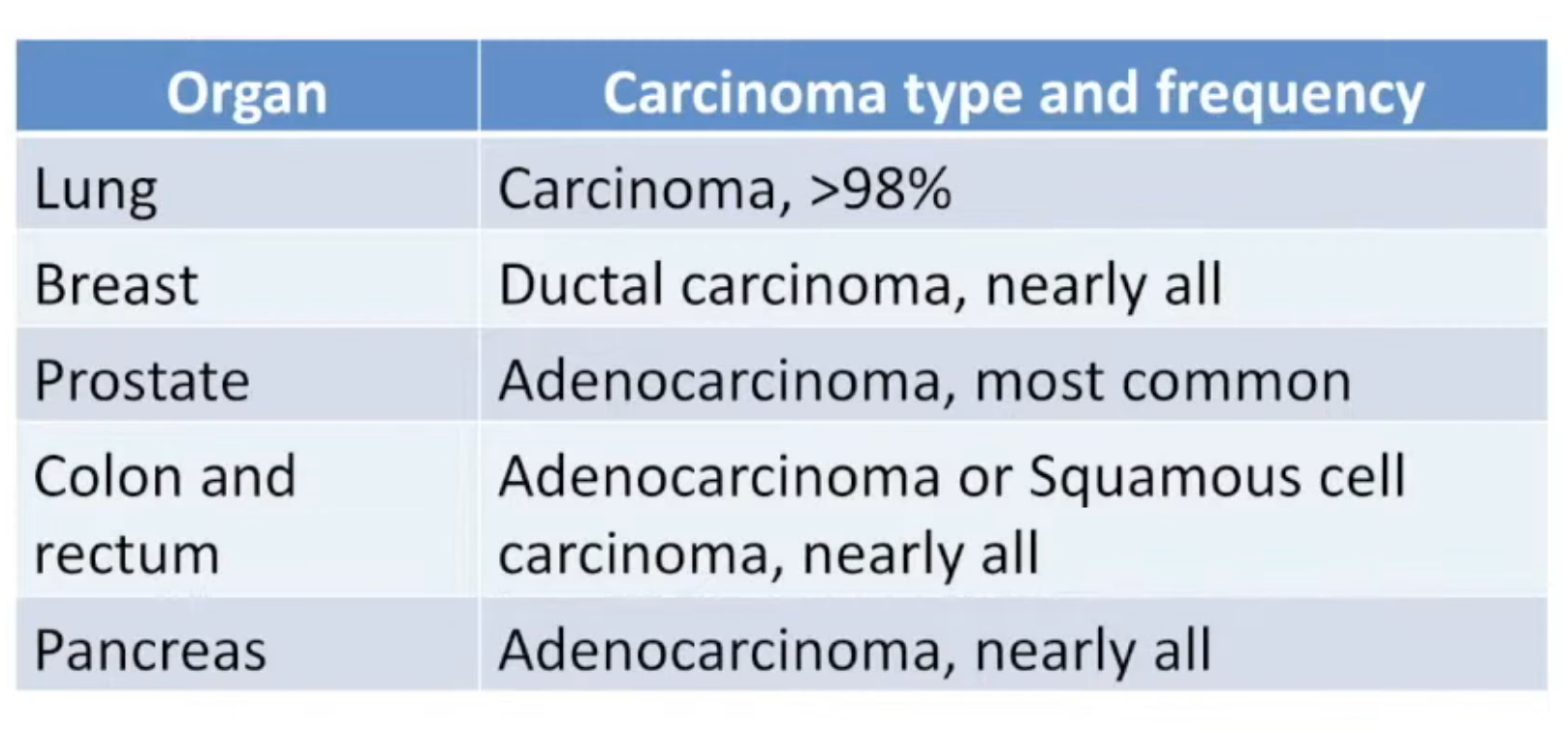
Here’s an explanation of each type of cancer: 1. Carcinomas: Carcinomas are cancers that arise from epithelial cells, which line the surfaces of organs, glands, and other structures in the body. Common Locations: Skin, lungs, breast, prostate, colon, and pancreas. Subtypes:
Carcinomas are the most common type of cancer in adults.
2. Sarcomas: Sarcomas are cancers that arise from connective tissues, including bones, muscles, fat, cartilage, and blood vessels. Common Locations: Bones, muscles, and soft tissues of the body. Subtypes:
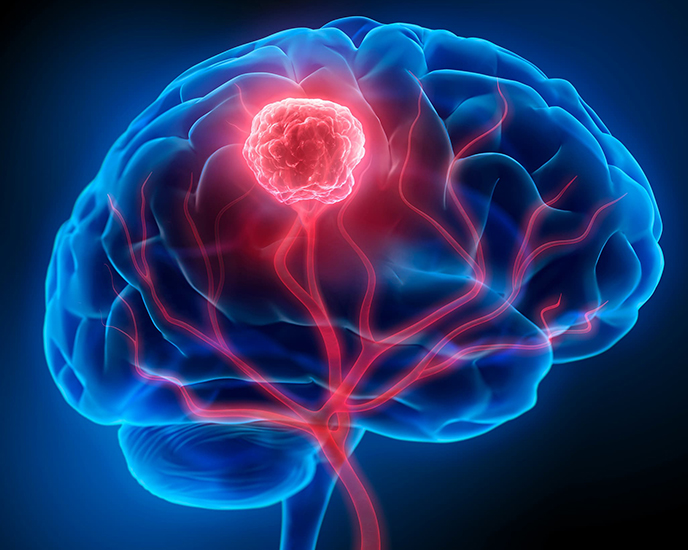
Characteristics: Sarcomas are rare compared to carcinomas and can be aggressive, often spreading to lungs. 3. Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors: These are tumors that arise within the brain or spinal cord. They can be benign or malignant. Common Types:
Characteristics: CNS tumors may not always spread to other parts of the body, but their location can make them life-threatening due to pressure on the brain or spinal cord. 4. Germ Cell Tumors: Germ cell tumors originate from the reproductive cells (germ cells), which are involved in reproduction (sperm or egg cells). Common Locations: Ovaries, testes, and sometimes in other areas like the brain (extragonadal germ cell tumors). Subtypes:
Characteristics: Germ cell tumors can be benign or malignant and are often detected in young adults and adolescents. Key Differences at a Glance: Type of Tumor Origin Common Locations Characteristics
These distinctions are crucial for diagnosis, treatment planning, and prognosis. For instance, carcinomas are more likely to be treated with surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, while sarcomas might require specialized surgical approaches due to their tissue of origin. CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW |
|
CANCER - ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW |
Oncology (Cancer) & Nuclear Medicine
This site has been developed for Cancer Patients & their Relatives under the 'Right of information for Patients'.
You may translate this page by clicking on the 'Select Language' - Top Left.